
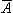
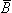
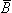 LM
LM


 LE
LE LM
LM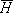
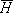 LM
LM
 dv
dv i
i i,
i,  o
o iF,
iF,  iV
iV ir,
ir,  it
it L
L LE
LE LI
LI LM
LM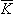 j
j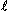
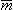
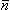
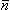 j
j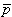



Symbols and Units
| ah, am, an | transfer rate coefficients (Hodgkin-Huxley model) |
| bh, bm, bn | - " - |
| ds, dv | two-dimensional [m-2] and three-dimensional [m-3] Dirac delta functions |
| e | permittivity [F/m] |
| E | electromotive force (emf) [V] |
| Q | conduction velocity (of wave) [m/s] |
| l | membrane length constant [cm] (~ Ö(rm/ri) = Ö(Rma/2ri)) |
| µ | magnetic permeability of the medium [H/m = Vs/Am] |
| µ, µ0 | electrochemical potential of the ion in general and in the reference state [J/mol] |
| n | nodal width [µm] |
| r | resistivity [Wm], charge density [C/m3] |
| rib, rob | intracellular and interstitial bidomain resistivities [kW·cm] |
| rmb | bidomain membrane resistivity [kW·cm] |
| rtb | bidomain total tme impedance [kW·cm] |
| ri, ro | intracellular and interstitial resistivities [kW·cm] |
| s | conductivity [S/m] |
| sib, sib | intracellular and interstitial bidomain conductivities [mS/cm] |
| si, so | intracellular and interstitial conductivities [mS/cm] |
| t | membrane time constant [ms] (= rmcm in one-dimensional problem, = RmCm in two-dimensional problem) |
| f, q | longitude (azimuth), colatitude, in spherical polar coordinates |
| F | potential [V] |
| Fi, Fo | potential inside and outside the membrane [mV] |
| FLE | reciprocal electric scalar potential field of electric lead due to unit reciprocal current [V/A] |
| FLM | reciprocal magnetic scalar potential field of magnetic lead due to reciprocal current of unit time derivative [Vs/A] |
| F, y | two scalar functions (in Green's theorem) |
| c | surface to volume ratio of a cell [1/cm] |
| w | radial frequency [rad] (= 2pf ) |
| W | solid angle [sr (steradian) = m2/m2] |
| a | radius [m], fiber radius [µm] |
 | unit vector |
| A | azimuth angle in spherical coordinates [ ° ] |
| A | cross-sectional area [m²] |
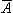 | magnetic vector potential [Wb/m = Vs/m] |
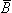 | magnetic induction (magnetic field density) [Wb/m2 = Vs/m2] |
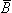 LM LM | reciprocal magnetic induction of a magnetic lead due to reciprocal current of unit time derivative [Wb·s/Am2 = Vs2/Am2] |
| c | particle concentration [mol/m3] |
 | lead vector |
| ci,co | intracellular and extracellular ion concentrations (monovalent ion) [mol/m3] |
| ck | ion concentration of the kth permeable ion [mol/m3] |
| cm | membrane capacitance per unit length [µF/cm fiber length] |
| C | electric charge [C (Coulomb) = As] |
| Cm | membrane capacitance per unit area (specific capacitance) [µF/cm²] |
| d | double layer thickness, diameter [µm] |
| di,do | fiber internal and external myelin diameters [µm] |
d | outward surface normal |
| D | Fick's constant (diffusion constant) [cm2/s = cm3/(cm·s)] |
| D | electric displacement [C/m2] |
| E | elevation angle in spherical coordinates [ ° ] |
 | electric field [V/m] |
 LE LE | reciprocal electric field of electric lead due to unit reciprocal current [V/Am] |
 LM LM | reciprocal electric field of magnetic lead due to reciprocal current of unit time derivative [Vs/Am] |
| F | Faraday's constant [9.649·104 C/mol] |
| F | magnetic flux [Wb = Vs] |
| gK, gNa, gL | membrane conductances per unit length for potassium, sodium, and chloride (leakage) [mS/cm fiber length] |
| GK, GNa, GL | membrane conductances per unit area for potassium, sodium, and chloride (leakage) [mS/cm2] |
| GK max, GNa max | maximum values of potassium and sodium conductances per unit area [mS/cm2] |
| Gm | membrane conductance per unit area [mS/cm2] |
| h | distance (height) [m] |
| h | membrane thickness [µm] |
| h, m, n | gating variables (Hodgkin-Huxley model) |
| Hct | hematocrit [%] |
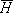 | magnetic field [A/m] |
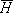 LM LM | reciprocal magnetic field of a magnetic lead due to reciprocal current of unit time derivative [s/m] |
| im | membrane current per unit length [µA/cm fiber length] (= 2paIm) |
| ir | reciprocal current through a differential source element [A] |
| I | electric current [A] |
| Ia | applied steady-state (or stimulus) current [µA] |
| Ii, Io | axial currents [µA] and axial currents per unit area [µA/cm2] inside and outside the cell |
| iK, iNa, iL | membrane current carried by potassium, sodium, and chloride (leakage) ions per unit length [µA/cm fiber length] |
| IK, INa, IL | membrane current carried by potassium, sodium, and chloride (leakage) ions per unit area [µA/cm²] |
| IL | lead current in general [A] |
| Im | membrane current per unit area [µA/cm2] (= ImC + ImR), bidomain membrane current per unit volume [µA/cm³] |
| imC, imI, imR | capacitive, ionic, and resistive components of the membrane current per unit length [µA/cm fiber length] (= 2paImC , = 2paImI , = 2paImR ) |
| ImC, ImI, ImR | capacitive, ionic, and resistive components of the membrane current per unit area [µA/cm²] |
| Ir | total reciprocal current [A] |
| Irh | rheobasic current per unit area [µA/cm2] |
| Is | stimulus current per unit area [µA/cm2] |
| j, jk | ionic flux, ionic flux due to the kth ion [mol/(cm2·s)] |
| jD, je | ionic flux due to diffusion, due to electric field [mol/(cm2·s)] |
 | electric current density [A/m2] |
 dv dv | source element |
 i i | impressed current density [µA/cm2], impressed dipole moment per unit volume [µA·cm/cm3] |
 i, i,  o o | intracellular and interstitial current densities [µA/cm2] |
 iF, iF,  iV iV | flow (flux) and vortex source components of the impressed current density [µA/cm2] |
 ir, ir,  it it | radial and tangential components of the impressed current density [µA/cm2] |
 L L | lead field in general [A/m2] |
 LE LE | electric lead field due to unit reciprocal current [1/m2] |
 LI LI | lead field of current feeding electrodes for a unit current [1/m2] (in impedance measurement) |
 LM LM | magnetic lead field due to reciprocal current of unit time derivative [s/m2] |
| K | constant |
| K(k), E(k) | complete elliptic integrals |
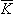 j j | secondary current source for electric fields [µA/cm2] |
| l | length [m], internodal spacing [µm] |
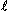 | liter |
| L | inductance [H = Wb/A = Vs/A] |
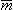 | magnetic dipole moment of a volume source [Am2] |
| M | vector magnitude in spherical coordinates |
| M1, M2, M3 | peak vector magnitudes during the initial, mid, and terminal phases of the QRS-complex in ECG [mV] and MCG [pT] |
| n | number of moles |
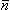 | surface normal (unit length) |
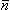 j j | surface normal of surface Sj directed from the primed region to the double-primed one |
| p | electric dipole moment per unit area [Am/m2 = A/m] |
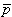 | electric dipole moment of a volume source [Am] |
| P | pressure [N/m²] |
| PCl, PK, PNa | membrane permeabilities of chloride, potassium and sodium iones [m/s] |
| r | radius, distance [m], vector magnitude in spherical polar coordinates |
| r | correlation coefficient |
 | radius vector |
| ri, ro | axial intracellular and interstitial resistances per unit length [kW/cm fiber length] (ri = 1/si pa2) |
| rm | membrane resistance times unit length [kW·cm fiber length] (= Rm/2pa) |
| R | gas constant [8.314 J/(mol·K)] |
| Ri, Ro | axial resistances of the intracellular and interstitial media [kW] |
| Rm | membrane resistance times unit area (specific resistance) [kW·cm2] |
| Rs | series resistance [MW] |
| SCl, SK, SNa | electric current densities due to chloride, potassium and sodium ion fluxes [µA/cm2] |
| t | time [s] |
| T | temperature [ ° C], absolute temperature [K] |
| u | ionic mobility [cm2/(V·s)] |
| v | velocity [m/s] |
| v | volume [m3] |
| V | voltage [V] |
| V ' | deviation of the membrane voltage from the resting state [mV] (= Vm - Vr ) |
| Vc | clamp voltage [mV] |
| VL | lead voltage in general [V] |
| VLE | lead voltage of electric lead due to unit reciprocal current [V] |
| VLM | lead voltage of magnetic lead due to reciprocal current of unit time derivative [V] |
| VK, VNa, VL | Nernst voltages for potassium, sodium, and chloride (leakage) ions [mV] |
| Vm | membrane voltage [mV] (= Fi - Fo) |
| Vr , Vth | resting and threshold voltages of membrane [mV] |
| VR | reversal voltage [mV] |
| VZ | measured voltage (in impedance measurement) [V] |
| W | work [J/mol] |
| X, Y, Z | rectangular coordinates |
| z | valence of the ions |
| Z | impedance [W] |
The List of Symbols and Units includes the main symbols existing in the book. Symbols, which appear only in one connection or are obvious extensions of those in the list, are not necessarily included. They are defined in the text as they are introduced.